IoT Device Management: Challenges, Solutions & Best Practices
Have you ever wondered how to keep tabs on thousands of interconnected devices spread across the globe? Remote IoT management is no longer a luxury but a necessity for organizations leveraging the power of connected devices. But this necessity comes with its own set of hurdles.
While the advantages of remote IoT management are undeniable, a significant number of challenges demand careful consideration and strategic solutions. Let's delve into some of the critical issues that businesses face when managing their IoT deployments from afar.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | IoT device management encompasses authentication, configuration, monitoring, maintenance, and diagnostics of connected devices. |
| Importance | Ensures device security, operational effectiveness, and reliability, minimizing downtime and maximizing performance. |
| Security | Requires secure channels for configuration and debugging, utilizing robust authentication and encryption. |
| Complexity | Developing effective IoT device management platforms is a complex, ongoing process. |
| Lifecycle | Covers the entire lifecycle of IoT devices, from provisioning to decommissioning. |
| Vulnerabilities | IoT devices are susceptible to hacking and data theft due to their network connectivity. |
| Mitigation | Secure configurations are crucial for protecting devices and data both in transit and at rest. |
| Efficiency | Forms the backbone of organized and efficient IoT networks, preventing unmanageability. |
| Maintenance | IoT software design must account for updates, repairs, and eventual decommissioning. |
| Connectivity | Remote management often necessitates public IP or fixed private IP solutions via private APNs. |
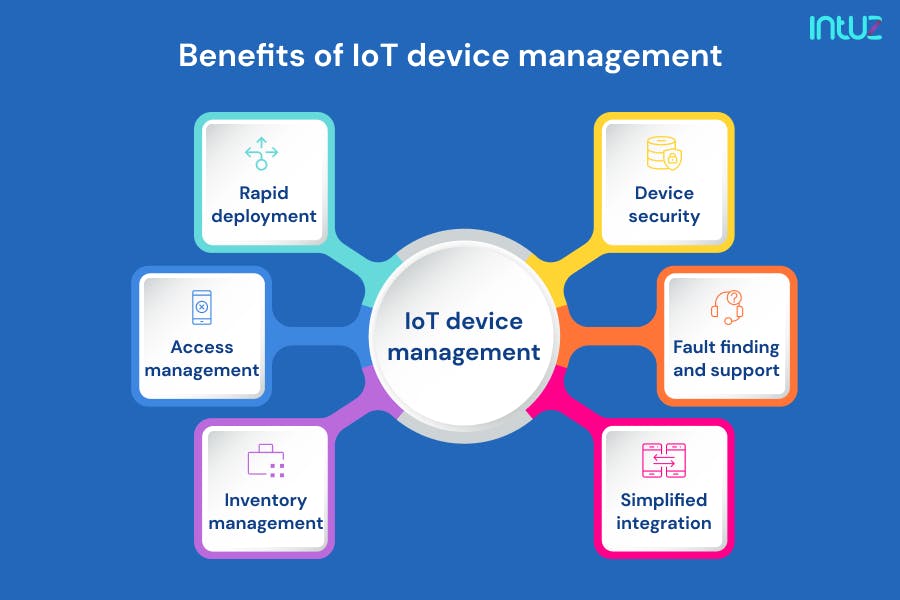
IoT device management is not merely a technical process; it is the linchpin of successful IoT deployments. It encompasses a wide array of tasks, from authenticating devices and configuring their settings to monitoring their performance and diagnosing any issues that may arise. It is the equivalent of a digital healthcare system for your connected devices, ensuring they remain healthy, secure, and functioning optimally.
- Frank Gallaghers Death Exploring The Shameless Finale Legacy
- Adriana Limas Kids A Glimpse Into Her Family Life Updated
The ultimate goal of effective IoT device management is to ensure that devices remain secure against unauthorized access, operate reliably under various conditions, and achieve optimal performance, minimizing downtime and maximizing their utility. It's about creating a robust and resilient network of interconnected devices that can deliver the promised benefits of IoT without exposing the organization to undue risks.
IoT device administrators and support teams face a constant challenge: How to securely configure, debug, and manage devices without compromising the integrity of the network. This necessitates the establishment of secure channels that employ robust authentication mechanisms and encryption protocols, safeguarding against unauthorized access and potential cyber threats. It is a high-stakes game of cat and mouse, where vigilance and robust security measures are the only guarantee of protection.
Creating a robust IoT device management platform is no small feat. It involves integrating a multitude of features, including device provisioning, configuration management, performance monitoring, remote control capabilities, and comprehensive security measures. Such platforms must be able to handle a diverse range of devices, communication protocols, and data formats while providing a user-friendly interface for administrators and support teams. It is a complex engineering undertaking that requires expertise in software development, networking, cybersecurity, and data analytics.
- Asma Assad From First Lady To Exile The Assad Story
- Emmas Fortune Net Worth Of Watson Chamberlain More
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Smart Waste Management | Utilizes technology and data to enhance waste industry efficiency. |
| Technology | Based on IoT (Internet of Things) technology. |
| Objectives | Optimizes resource allocation, reduces costs, and increases sustainability of waste services. |
As the IoT landscape continues to evolve, so too must the strategies and tools used to manage it. A comprehensive IoT device management strategy is essential for maintaining control over deployed devices, ensuring their security, and maximizing their value. Without such a strategy, organizations risk losing sight of their connected devices, leaving them vulnerable to cyber threats and operational inefficiencies.
These platforms are typically loaded with a suite of features designed to streamline the entire device lifecycle. Device provisioning allows for the seamless setup of new devices, while configuration management enables administrators to customize device settings and behaviors. Performance monitoring provides real-time insights into device health and performance, and remote control capabilities allow for troubleshooting and maintenance from afar. It's like having a virtual command center for your entire IoT ecosystem.
IoT device management provides a centralized point of control over the entire lifecycle of IoT devices, from initial deployment to eventual decommissioning. This includes device provisioning, configuration, monitoring, maintenance, security patching, and software updates. By managing these tasks centrally, organizations can ensure that their IoT devices are always up-to-date, secure, and performing optimally. This centralized approach also simplifies troubleshooting and reduces the risk of human error.
A critical aspect of IoT device management is understanding the access modes and protocols supported by different devices. This includes identifying the communication protocols used by devices, such as MQTT, CoAP, and HTTP, as well as the authentication methods employed to verify device identity. By understanding these aspects, administrators can ensure seamless communication between devices and the management platform, as well as implement appropriate security measures to protect against unauthorized access.
IoT devices, by their very nature, are small computers connected to a common network, making them vulnerable to hacking and data theft. Without proper security measures in place, hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in IoT devices to gain access to sensitive data, disrupt operations, or even use the devices as entry points into the broader network. This underscores the critical importance of implementing robust security measures from the outset of any IoT project.
To mitigate these risks, IoT projects must implement secure configurations to protect devices, data in transit, and data at rest. This includes using strong passwords, enabling encryption, implementing access controls, and regularly patching software vulnerabilities. By taking these steps, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of cyberattacks and protect their IoT deployments from harm.
In simple terms, IoT device management is the backbone that keeps IoT networks organized and efficient. It provides the tools and processes needed to manage a large number of connected devices, ensuring that they are properly configured, securely managed, and performing optimally. Without it, managing hundreds or thousands of IoT devices can quickly become an unmanageable and chaotic endeavor.
Imagine trying to manage hundreds or thousands of interconnected devices without a centralized management system. It would be like trying to herd cats: chaotic, inefficient, and ultimately unproductive. IoT device management provides the structure and control needed to effectively manage these devices, ensuring that they are working together seamlessly to achieve the desired outcomes.
As the number of connected devices in an IoT ecosystem continues to grow, the challenge of managing them effectively becomes increasingly complex. Without a robust device management strategy in place, organizations risk losing control over their IoT deployments, exposing themselves to security vulnerabilities, operational inefficiencies, and ultimately, financial losses.
IoT software should be designed with device lifecycle management in mind, including updates, repairs, and eventual decommissioning. This ensures that devices can be easily updated with the latest security patches and features, repaired when necessary, and securely decommissioned when they reach the end of their useful life. By managing the entire device lifecycle, organizations can minimize risks and maximize the value of their IoT investments.
IoT devices have the potential to transform the way we work, live, and interact with the world around us. From smart homes and connected cars to industrial automation and precision agriculture, IoT is revolutionizing industries and creating new opportunities for innovation. However, to fully realize the potential of IoT, organizations must have a deep understanding of IoT devices and their connectivity systems.
To effectively tackle device maintenance and remote management, it is often necessary to use public IP or fixed private IP solutions via private APNs that are not available to the general public. This provides a secure and reliable connection to devices, allowing administrators to remotely diagnose and resolve issues without compromising network security. It's like having a private tunnel to your devices, ensuring secure and reliable communication.
A comprehensive guide for enhanced device management provides a thorough examination of the principles and practices involved in effectively monitoring and managing devices remotely. This equips readers with the knowledge and skills needed to optimize their remote management strategies, elevate their device management capabilities, and ensure the security and reliability of their IoT deployments.
Mobile device management (MDM) is an essential technology for managing and securing mobile devices within an organization. With the rise of mobile workforces and the growing reliance on mobile devices for business operations, MDM has become a critical tool for ensuring the security and functionality of mobile endpoints. It provides organizations with the ability to remotely configure, monitor, and manage mobile devices, ensuring that they are compliant with security policies and operating efficiently.
A poor device management approach can leave businesses vulnerable to cyberattacks. Cybercriminals can exploit vulnerabilities in poorly managed devices to gain access to sensitive data, disrupt operations, or even use the devices as launching pads for botnets and other types of cyberattacks. This underscores the importance of implementing robust device management practices to protect against these threats.
Protecting IoT medical devices is particularly important, even though most do not store much personal data. These devices are often connected to critical systems and used to monitor patient health, making them attractive targets for hackers. A successful attack on an IoT medical device could have serious consequences, potentially compromising patient safety and disrupting healthcare operations.
The term IoT encompasses a vast network of physical devices, ranging from simple household items to complex industrial tools, each connected to the digital universe in its unique way. This interconnectedness is what gives IoT its power, enabling devices to communicate with each other, share data, and automate tasks. However, it also creates new challenges for device management and security.
The roots of IoT can be traced back to the 1990s, when the idea of embedding computing power into everyday objects began to take shape. Early examples of IoT devices included vending machines that could report their inventory levels and environmental sensors that could monitor temperature and humidity. These early innovations laid the foundation for the explosion of IoT devices that we see today.
IoT has the potential to eliminate ambiguity between fleet operators and drivers, leading to better working relationships and improved operational efficiency. By providing real-time visibility into vehicle location, driver behavior, and other key metrics, IoT enables fleet operators to make data-driven decisions that optimize performance and reduce costs. It's a win-win for both operators and drivers, leading to a more productive and efficient transportation system.
Google Cloud IoT is a platform that enables businesses to securely connect and manage IoT devices, collect and analyze data, and build custom IoT applications. It provides a comprehensive set of tools and services for managing the entire IoT lifecycle, from device provisioning to data analytics. With Google Cloud IoT, businesses can quickly and easily deploy and manage IoT solutions at scale, accelerating innovation and driving business value.
Integration of IoT in energy management enhances energy management by providing real-time data on energy consumption, enabling organizations to identify opportunities for optimization and reduce waste. By connecting energy-consuming devices to the IoT, businesses can gain valuable insights into their energy usage patterns, allowing them to make informed decisions that lower costs and improve sustainability.
Auxilium is a company specializing in alarms. While not directly related to IoT device management, companies like Auxilium play an important role in the broader IoT ecosystem by providing security solutions that protect connected devices and networks. As IoT deployments become more widespread, the need for robust security solutions will only continue to grow.
- Find Hindi Dubbed Movies Shows Online Your Guide
- Taurus Scorpio Friendship Compatibility Challenges More

The Ultimate Guide to IoT Device Management in 2024

IoT Device Management Platform The Ultimate Guide
The Ultimate Guide to IoT Device Management in 2024